The Energy Transition Plan was updated in 2023, in the light of the current energy context
Cellnex is aware of the importance of its energy performance and the sustainable origin of the energy needed for its operations. In this context, indirect emissions from electricity consumption significantly contribute to Cellnex's carbon footprint.
To boost this awareness, specific Energy Guidelines were issued in 2021, further developed in 2022, and evolved in 2023, taking account of the current energy context. The guidelines state that Cellnex promotes the efficient use of energy through the implementation of energy-saving and efficiency measures in work processes and conduct, and by controlling and monitoring consumption in the most significant applications. Additionally, as more than the 76% of Cellnex's total consumption is directly consumed by customer-owned equipment, Cellnex applies energy billing models to customers that promote efficiency in customers' equipment, using the pass-through mechanism.
All of this is based on compliance with applicable legal and regulatory standards at international, European, state, regional and local level, as well as the willingness to adapt to future standards, and the requirements of customers and society.
Energy 4.0 |
Green energy sourcing |
Energy efficiency |
Self-generationn |
To demonstrate its commitment to responsible consumption and proper energy management, in 2021 Cellnex adopted an Environment and Climate Change Policy, updated in 2023, specifying its commitments relating to efficient energy management:
To comply with these commitments, in 2021 Cellnex released the first version of its Energy Transition Plan as part of its ESG Master Plan and the Strategic Sustainability Plan. This plan was updated in 2023, taking account of the current energy context.
The Energy Transition Plan has four pillars:
In 2023, Cellnex met its renewable electricity consumption with
77 %
of consumption from renewable sources
Cellnex is also reviewing the greening journey with customers to ensure a feasible path also for them, considering the pass-through model.
|
Energy Transition Plan Targets |
||
|
Deploying Global Energy Platform for 70% of Cellnex's consumption by 2025 |
100% green electricity consumption by2025. |
The 70% of Cellnex consumption to be ISO 50001 certified by 2025. |
During 2021 Cellnex released the first version of its Energy Transition Plan, focused on defining the scope and overall strategy, but only with regard to delivering commitments under the Green Energy Sourcing pillar. However, in 2022 and 2023 Cellnex continued developing the overall strategy of intensifying the key activities and outlined corporate commitments to pave the way to carbon-neutral operations. In addition, a budget plan was allocated to investment and development for the four pillars of the Energy Transition Plan.
The Group's total energy consumption for 2023 was 1,390.22 GWh (1,301.18 GWh in 2022), most of which was electricity consumption. Cellnex's sites account for most electricity consumption and its offices to a lesser extent. In 2023 the total electricity consumed was 1,384.27 GWh (1,295.12 GWh in 2022), 77% of which came from renewable sources.
Detailed information on energy consumption is available in Annex 6. KPI Tables

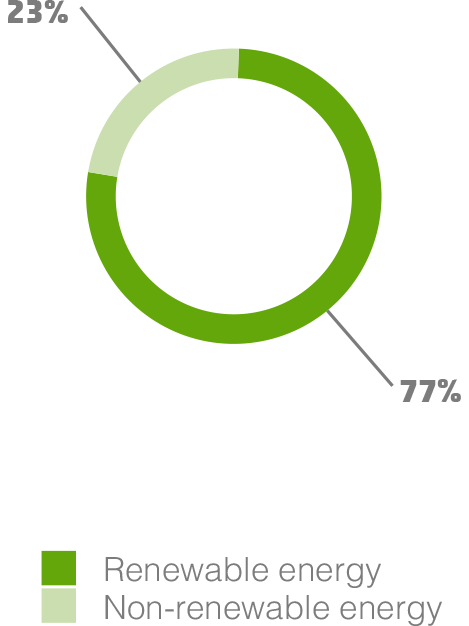
77 %
renewable electricity
As a result of the green energy sourcing strategy, the share of renewable electricity has increased in recent years from 10% in 2020 to 77%% in 2023.
|
2023 |
2022 |
|
 |
na |
na |
 |
100 % |
100 % |
 |
100 % |
100 % |
 |
— % |
— % |
 |
58 % |
59 % |
 |
100 % |
100 % |
 |
93 % |
94 % |
 |
na |
na |
 |
100 % |
100 % |
 |
100 % |
100 % |
 |
100 % |
100 % |
 |
100 % |
100 % |
Together with its customers, Cellnex is promoting energy efficiency and self-generation measures.
As a result of investments made in energy saving and efficiency measures, in 2023 it succeeded in cutting energy consumption, as indicated below.
|
|
Energy saved (GWh) |
Investment (thousands of EUR) |
|
Cooling |
0.0 |
0 |
|
Fuel |
0.8 |
0 |
|
Electricity |
1.6 |
2,719 |
|
Total |
2.4 |
2,719 |
Nexloop is committed to selecting air conditioners with maximum efficiency and minimal energy consumption during obsolescence or facility transformations.
As part of their green initiative, hybrid vehicles have been incorporated into the vehicle fleet. Taking a significant step towards sustainability, Cellnex France has transitioned the electricity supply contract for the Boulogne headquarters to a renewable energy source.
Cellnex Ireland completed the installation of 64 solar photovoltaic systems supplying electrical energy to the on-site base station equipment, producing approximately 320 MWh of sustainable green energy over the course of 2023.
Cellnex Netherlands has become a participant in EU Taxonomy Data Centres, aiming to meet the EU’s climate and energy targets for 2030.
Moreover, Cellnex Netherlands, has joined the European Code of Conduct on Data Centres as a participant. The organisation is expecting to implement best practices and monitor energy consumption, while regularly reporting to the EU Commission.
Cellnex Poland continued with the modernisation of BBUs (DC power systems) by replacing the rectifiers with more efficient models and installing reactive power compensators. Furthermore, a solar panel pilot has been implemented at three sites, and according to the responsible company's declaration, it has been estimated that these panels will produce an average of 10% of its demand.
In 2023, Cellnex Spain has been at the forefront of energy-efficiency initiatives, notably the deployment of photovoltaic panels at various locations. Noteworthy efforts include piloting hydrogen batteries, upgrading cooling equipment, and implementing advanced systems for monitoring and controlling consumption.
A pivotal highlight of Cellnex's endeavours in 2023 involves a robust campaign aimed at replacing diesel generator-powered sites with an innovative solution featuring solar panels and compact generators. This strategic move has resulted in a substantial reduction in the carbon footprint, showcasing Cellnex's commitment to sustainable practices.
Water is consumed throughout the Cellnex Group primarily for sanitation. Water for the whole Group is provided mainly through the public water supply network, with a total consumption of 13,615 m3. This year, the water consumption figure has increased due to improved data collection, incorporating consumption from Austria, France, and Switzerland.
Moreover, in 2023 the Group's water footprint was calculated and audited in line with the methodology defined in ISO 14046. Although Cellnex's consumption is a non-material issue for the Company due to the nature of its activity, Cellnex aims to calculate its water footprint annually to monitor and control the impact of Cellnex's activity on this resource.
In terms of discharges, Cellnex only discharges sanitary water that can be assimilated to domestic water into the sewage network in general, and in very few cases in Spain, into duly legalised septic infiltration pits.
Waste generated at Cellnex sites during construction, operation, maintenance, and decommissioning operations is managed by waste management providers. To ensure that this management is carried out properly, Cellnex ensures that any waste produced by its suppliers in the course of outsourced activities is treated properly. In addition, Cellnex promotes proper waste management throughout the Company and its value chain, taking the waste hierarchy into account, thereby fostering waste prevention and preparing it for reuse and recycling.
As a circular economy initiative, Cellnex has donated obsolete equipment (258 mobile phones and 463 pieces of IT equipment) to l'Associació Cívica La Nau to be reused. This initiative has prevented the generation of 746,92 kg of electronic waste and 129,15 tCO2.
In the Cellnex Group, various initiatives are being implemented to promote the circular economy and reduce waste as much as possible. They emphasise re-use over disposal and encourage suppliers to prioritise these management methods as well.
Cellnex countries have undertaken numerous activities related to the circular economy, primarily focused on reducing the quantity of generated waste, prioritising its management and valorisation.
In 2023, the Cellnex Spain Environment Department initiated the analysis in collaboration with Logistics for the recovery of WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment). The goal is to negotiate with a company specialising in recovering such devices, giving them a second life and preventing them from becoming waste. The objective is to reduce the amount of waste (WEEE) generated by promoting reuse and putting them back onto the market.
Cellnex Portugal promoted the reuse of some of its towers, which were replaced by higher capacity towers in their original location but that were still usable in other areas with lower capacity demands. This not only reduces the amount of waste, but also the lengthens the life cycle of the infrastructure to its full potential.
Cellnex's vision is to transform the existing paradigm to reduce the environmental impact of its TIS centers in Europe. In 2020, they initiated a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) project for these centers to identify inputs and outputs throughout their life cycle.
In 2022, Cellnex updated this project with the Eco-design project, establishing two eco-design models for rural and rooftop TIS centers, considering technical and legal barriers for each of them and the proposed eco-design strategies.
To this end, an eco-design checklist was drawn up to help reduce:
The eco-design checklist was drawn up by applying ISO 14006. The most notable aspects of the design and development process for a TIS centre contained in the eco-design checklist are:
To this end, Cellnex has established a green procurement protocol, defining a list of sustainability and circularity criteria to facilitate decision-making related to the evaluation and selection of providers that operate the IT centres. In this regard, aspects such as eco- design, consumption of raw materials, energy consumption, emissions, waste generation, impact on biodiversity, and social and economic impact are taken it.
Based on the scenarios identified in the Eco-design project, an Eco-design group was formed in 2023 to collectively develop proposals to add environmental criteria to Cellnex's operations and maintenance. The group was attended by colleagues from Spain, Poland, France, Sweden, Italy, and Austria. The proposals were discussed jointly addressing topics such as energy efficiency technologies, reuse and recycling of materials, implementation of renewable energies, use and collection of batteries, use of fuels, and new eco-design proposals.
On the other hand, in 2023, a Life Cycle Assessment of datacentres has been carried out, with the aim of identifying where the main impacts are in all phases of the life cycle of this service, in order to be able to define in 2024, eco-strategies and initiatives to make the datacentre activity more circular. The main conclusions of the datacentre LCA are:
Before starting...
We use our own and third-party cookies for analytical purposes and to show you personalized advertising based on a profile prepared from your browsing habits (for example, pages visited). Click HERE for more information. You can accept all cookies by pressing the "Accept" button or configure or reject their use by pressing the "Configure" button.
ACCEPT AND CONTINUE Configure cookies