Cellnex operates in accordance with international reference standards and voluntary initiatives
Cellnex has a Global Risk Management Policy approved by the Board of Directors that sets out the group-level risk strategy. The approval of this policy also established the strategy for Global Risk Management and its commitment to the application of best practices in the countries in which the Company operates, based, in turn, on international reference standards.
Cellnex operates in accordance with international reference standards and voluntary initiatives that include, among others:
The Global Risk Management function is based on
Account is also taken of the provisions of the Company's global Integrated Management System and the requirements of the ISO standards in which it is going to be certified in terms of risk management. In that connection, the Global Risk Management Policy highlights the Company's efforts to mitigate inherent risks that may affect the business, thus guaranteeing the continuity of each of its projects and actions. It also promotes the creation of sustained value in the short, medium and long term for all the company's stakeholders, while demonstrating its commitment to reducing adverse impacts on economic activity.
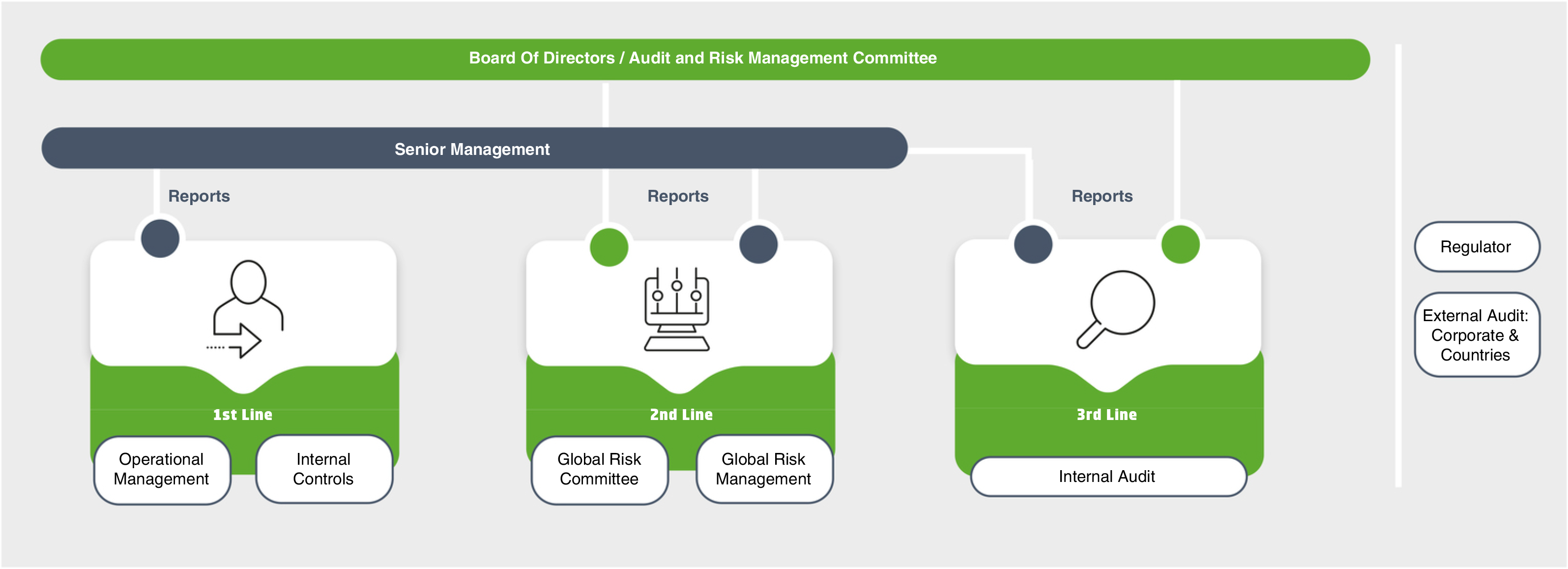
Cellnex's Board has focused its work on defining the risk management strategy, supervising its application and monitoring it, as well as promoting best corporate governance practices. As a function entrusted by the Board, the Audit and Risk Management Committee (ARMC) supervises the effectiveness of the Global Risk Management Model and the information provided to third parties, and must ensure that the risk management framework identifies, prioritises, controls, monitors, and reports them properly. A Global Risk Committee was established in 2022, including members from all functional Corporate departments and advised by the internal audit unit. In 2023, three Global Risk Committee meetings were held, covering the following main topics:
The Global Risk Management department is the main one responsible for the optimal deployment of the risk management methodology within the organisation, ensuring monitoring and compliance. The Global Risk Management function is based on anticipation, independence and commitment to the Group's business objectives, guaranteeing the robustness of the Global Risk Management Model through a risk assessment methodology aligned and adapted to the needs of the risk function and of the Company
Risks are events that may have an impact on the achievement of the strategic objectives established by the Board of Directors, so they must always be considered for risk management in order to guarantee the resilience of the organisation.
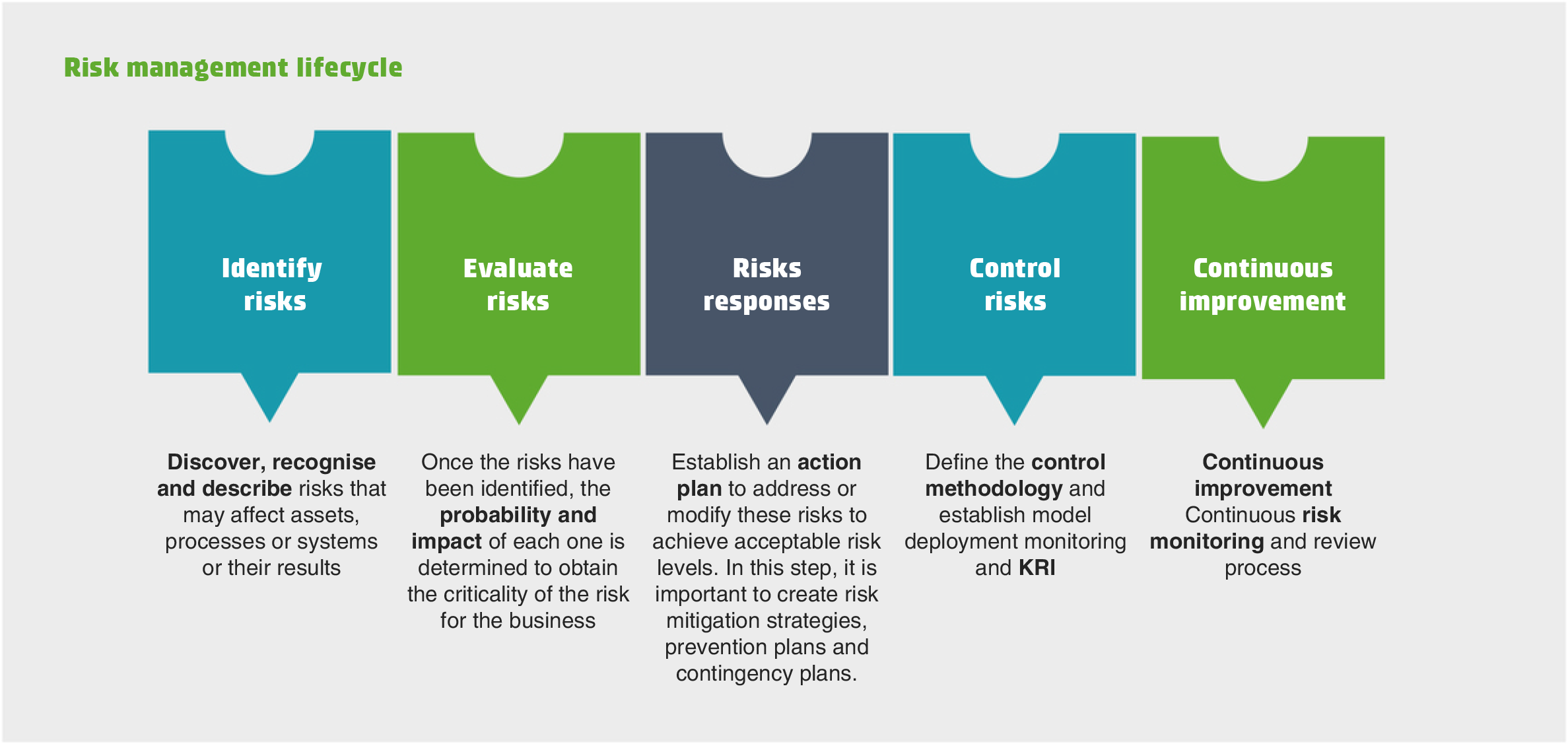
In order to carry out correct risk management, it is important to analyse both external and internal factors that could lead to an event having an impact on the Cellnex Group's objectives.
The governance of the Global Risk Management Model is configured taking the best international practices as a reference. It is based on a combined assurance around the Three Lines Model, providing an integrated vision of how the different parts of the Cellnex Group organisation interact effectively and in a coordinated manner, making the Group's risk management and internal control processes more efficient.The Global Risk Management framework is based on the application of the Three Lines Model:
Cellnex is currently developing a new Global Risk Management Master Plan 2024-2026, featuring three strategic lines (resilience, anticipation, and risk culture) and five key initiatives (risk assessment, internal control model, communication and awareness, governance model, and SAP GRC implementation). Those three modules are already in production in SAP GRC, and internal control campaigns for ICFR (SCIIF in Spanish), TAX, and Compliance have been launched, along with Cellnex’s general Entity Level Controls (ELC).
The Business Continuity Framework was fully defined (policy, scope, etc.) in 2023, along with the analysis phases (BIA, risk assessment), design (continuity strategies, mitigation controls), and implementation (response teams, BCPs, DRPs). There's a special focus on the crisis management plan, which will include dissemination of the plan and a corporate-level drill in 2023. The Business Units will conduct these drills in 2024.
Regarding the Risk Management Communication Plan, training and awareness-raising actions regarding the new risk management methodology were carried out in 2023 with the Risk Partners, to support them as Second Line. In addition, training and awareness-raising actions on the new risk management methodology were also carried out in the corporate departments during the risk assessment process.
Cellnex’s risk department has also been working closely with its ESG department throughout 2023 to anticipate and adapt to the new way of conducting non-financial reporting according to CSRD/ESRS in a joint and coordinated manner. The ESRS emphasise the critical role of risk management, underlining the paramount importance for companies to remain prepared and proactive in addressing potential risks and uncertainties.
There follows a list of the main risks that may affect Cellnex Group business and the achievement of its objectives.
|
Strategic risks |
I) |
Risks related to the environment in which the Group operates and risks stemming from the specific nature of its businesses. |
|
II) |
Risks of increasing competition. |
|
|
III) |
The Group’s status as a “significant market power” (SMP) operator in the digital terrestrial television (DTT) market in Spain imposes certain detrimental obligations on it compared with its competitors. |
|
|
IV) |
Industry trends and technological developments may require the Group to continue investing in adjacent businesses to telecommunication towers, such as fibre, edge computing and small cells. |
|
|
V) |
Spectrum is a scarce resource and it is highly dependent on political decisions. Access may not be secured in the future, which would prevent the Group from providing a high portion of its services in accordance with its plans. |
|
|
VI) |
Risk related to a substantial portion of Group revenue being derived from a small number of customers. |
|
|
VII) |
Risk of infrastructure sharing. |
|
|
VIII) |
Risk of non-execution of the entire committed perimeter. |
|
|
IX) |
The expansion or development of the Group's businesses, including through acquisitions or other growth opportunities, involve a number of risks and uncertainties that could adversely affect operating results or disrupt operations. |
|
|
X) |
Risks inherent in the businesses acquired and the Group’s international expansion. |
|
|
XI) |
Risk related to the non-control of certain subsidiaries. |
|
|
XII) |
Risks related to execution of Cellnex's acquisition strategy. |
|
|
XIII) |
Regulatory and other similar risks. |
|
|
XIV) |
Litigation. |
|
|
XV) |
Risk related to the Parent Company’s significant shareholders’ interests differing from those of the Group. |
|
|
Operational risks |
XVI) |
Risks related to the industry and the business in which the Group operates. |
|
XVII) |
Risk of not implementing the strategic sustainability plan. |
|
|
XVIII) |
Risks related to maintaining the rights over land where the Group’s infrastructures are located. |
|
|
XIX) |
Failure to attract and retain high quality personnel could adversely affect the Group’s ability to operate its business. |
|
|
XX) |
The Group relies on third parties for key equipment and services, and their failure to properly maintain these assets could adversely affect the quality of its services |
|
|
Financial risks |
XXI) |
Financial information. |
|
XXII) |
Expected contracted revenue (backlog). |
|
|
XXIII) |
Foreign currency risks. |
|
|
XXIV) |
Interest rate risk. |
|
|
XXV) |
Credit risk. |
|
|
XXVI) |
Liquidity risks. |
|
|
XXVII) |
Inflation risk. |
|
|
XXVIII) |
Risk related to the Group's indebtedness. |
|
|
XXIX) |
The Parent Company cannot guarantee that it will be able to implement its Shareholders' Remuneration Policy or to pay dividends (and even if it were able to, that it would do so). |
|
|
Compliance risks |
XXX) |
Fraud and compliance risks. |
|
XXXI) |
Risk associated with significant agreements signed by the Group that could be modified due to change-of-control clauses. |
Further detailed information, please see Annex 1. Risks.
Before starting...
We use our own and third-party cookies for analytical purposes and to show you personalized advertising based on a profile prepared from your browsing habits (for example, pages visited). Click HERE for more information. You can accept all cookies by pressing the "Accept" button or configure or reject their use by pressing the "Configure" button.
ACCEPT AND CONTINUE Configure cookies